AMD is making significant strides in optimizing the performance of its Ryzen 9000 series CPUs, particularly the Ryzen 9600X and 9700X models, with recent BIOS updates. These updates aim to address some of the latency issues that have been highlighted in reviews of the new Zen 5 architecture, which has faced mixed feedback since its launch. This move comes in conjunction with updates to Windows 11, specifically tailored to improve performance for AMD processors.
Addressing Core-to-Core Latency
Since the introduction of the Ryzen 9000 series, reviewers have pointed out higher-than-anticipated core-to-core latency in these processors. This is particularly noticeable in multi-CCD (Chiplet Die) configurations, which are characteristic of the Ryzen architecture. In response, AMD has rolled out a new BIOS optimization that is designed to reduce this latency.
The latest BIOS updates include the AGESA PI 1.2.0.2 firmware. AMD notes that this update targets specific “corner cases” where data transactions between cores can become inefficient, requiring multiple transactions to read and write data. With the new firmware, AMD claims to have halved the number of transactions needed in these scenarios, resulting in a noticeable reduction in core-to-core latency. This optimization is especially important for users who rely on multi-threaded workloads, where efficient communication between cores is critical for overall performance.
Performance Gains with 105-Watt Mode
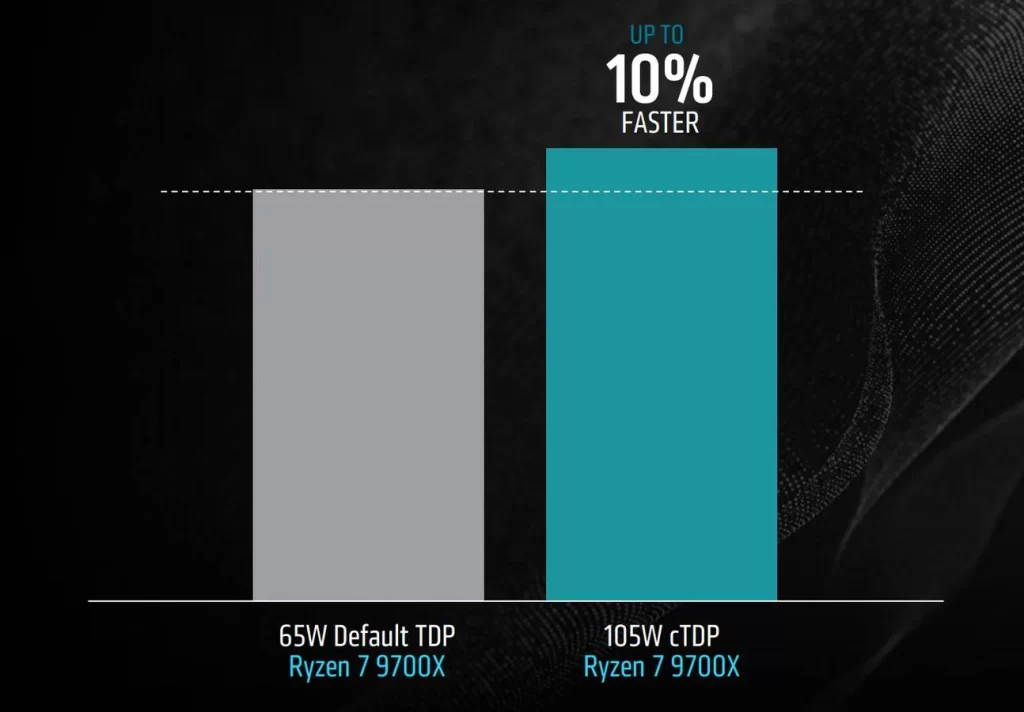
In addition to reducing latency, AMD is introducing a new 105-watt configurable thermal design power (cTDP) mode for the Ryzen 9600X and 9700X processors. This update promises a performance uplift of approximately 10 percent for these CPUs, particularly in multithreaded scenarios. AMD emphasizes that these processors have been validated for operation at 105W since their release, ensuring that users won’t be pushing the hardware beyond its designed limits.
To take advantage of the 105-watt mode, users will need to ensure their cooling systems are adequate, as increased power draw can lead to higher temperatures. AMD reassures customers that enabling this mode will not void the warranty, making it a compelling option for enthusiasts looking to extract more performance from their systems.
Windows 11 Updates for Optimized Performance
Alongside the BIOS updates, Microsoft is releasing Windows 11 enhancements aimed at improving performance for both Zen 4 and Zen 5 architectures. These updates focus on optimizing branch prediction for AMD-specific workloads, which can significantly impact the efficiency of CPU operations. Branch prediction is a crucial part of modern CPU architecture that helps determine the most likely path of execution for instructions, thereby improving speed and efficiency.
With these combined efforts from AMD and Microsoft, users can expect better overall system responsiveness and enhanced performance in various applications, especially those that are heavily reliant on multi-threaded processing.
New AM5 Motherboards: X870 and X870E
In addition to the BIOS updates, AMD is also launching its next-generation AM5 motherboards, the X870 and X870E models. These boards come with several advanced features, including standard USB 4.0 support and simultaneous PCIe 5.0 support for graphics and NVMe devices. Such capabilities are increasingly important as the industry gears up for the next generation of graphics cards, including anticipated releases like the RTX 5090, which are expected to leverage PCIe Gen 5 technology.
The X870 and X870E motherboards also provide support for higher-clocked memory, with AMD now enabling DDR5-8000 EXPO support on these new boards. This enhancement can deliver latency improvements of about 1 to 2 nanoseconds compared to DDR5-6000 memory, further elevating system performance for users who prioritize speed and efficiency.
The Importance of PCIe Gen 5 Support
The introduction of PCIe Gen 5 is particularly timely, as it allows for faster data transfer rates between the CPU and peripherals, including GPUs and storage devices. This is crucial for users who want to future-proof their systems, especially as software and games continue to evolve and demand more resources. With full PCIe Gen 5 support now available, AMD is positioning its platform as one that can accommodate the next wave of technological advancements in computing.
Conclusion
AMD’s latest BIOS updates and the introduction of new AM5 motherboards signify a strong commitment to enhancing the performance of its Ryzen 9000 series CPUs. By addressing core-to-core latency issues and providing a new 105-watt mode, AMD is ensuring that users can maximize their system’s potential without compromising stability or warranty. The collaboration with Microsoft to optimize Windows 11 further enhances the user experience, making AMD processors more competitive in the ever-evolving landscape of desktop computing.
As the market continues to grow and technology advances, these updates will be crucial for gamers, content creators, and professionals who rely on high-performance systems. With AMD’s focus on performance and efficiency, the Ryzen 9000 series is poised to remain a strong contender in the CPU market for the foreseeable future. Users looking to upgrade or build new systems will find that these enhancements, coupled with the latest hardware advancements, provide a compelling case for choosing AMD’s offerings.

