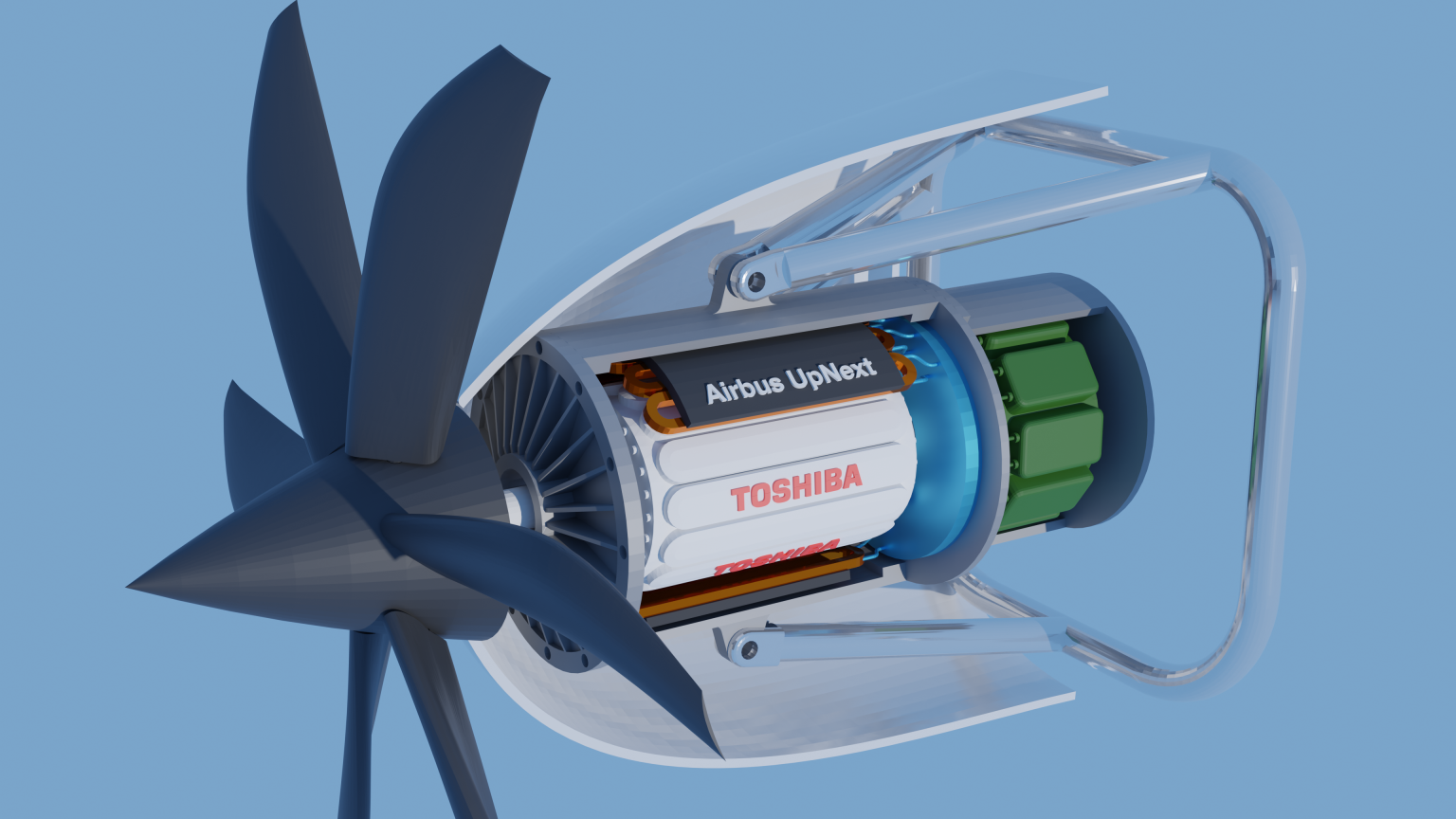
In a significant move toward sustainable aviation, Airbus and Toshiba have announced a collaboration aimed at developing superconducting technology specifically for hydrogen-powered aircraft. This partnership seeks to leverage Toshiba’s expertise in superconducting systems and Airbus’s advancements in electric propulsion, marking a pivotal step in the quest for net-zero emissions in aviation by 2050.
The Vision Behind the Partnership
Airbus has long been a leader in aerospace innovation, focusing on integrating advanced technologies into its aircraft designs. The collaboration with Toshiba is expected to enhance Airbus’s existing efforts in superconducting technologies, particularly for high-power electric propulsion systems. This partnership aims to conduct feasibility studies and develop a two-megawatt (2MW) superconducting motor that could significantly improve the efficiency and performance of future hydrogen-powered aircraft.
Grzegorz Ombach, Senior Vice President at Airbus, emphasized the unique opportunity presented by this partnership. He noted that the collaboration aims to surpass the capabilities of current electrical motors and conventional systems, ultimately unlocking new design possibilities for Airbus’s future aircraft.
Superconducting Technology Explained
Superconductivity involves the ability of certain materials to conduct electricity without resistance when cooled to extremely low temperatures. In the context of aviation, this technology holds immense promise for electric propulsion systems. The superconducting motors being developed will utilize liquid hydrogen as a coolant, maintaining temperatures around -253°C. This cryogenic technology can vastly enhance energy transmission, improving both aircraft performance and sustainability.
The integration of superconducting systems is expected to lead to significant advancements in energy efficiency, reduced emissions, and ultimately a shift toward more sustainable aviation practices. By collaborating with Toshiba, Airbus aims to harness these benefits effectively.
Advancements in Electric Propulsion
Airbus has been proactive in advancing superconducting technologies for high-power electric propulsion. In a notable achievement last year, the company successfully powered a 500 kW integrated cryogenic propulsion system. This milestone demonstrates Airbus’s commitment to innovation in electric propulsion, setting the stage for the development of even more powerful systems.
The new collaboration with Toshiba will build upon these advancements, focusing on the design and testing of a 2MW superconducting motor. Such a motor has the potential to revolutionize the way aircraft are powered, particularly in the emerging field of hydrogen aviation.
The Role of Hydrogen in Sustainable Aviation
Hydrogen-powered aircraft represent a promising avenue for achieving net-zero emissions in aviation. Airbus is actively working on its ZEROe project, which aims to bring the world’s first commercial hydrogen-fueled aircraft to market by 2035. The project explores two main approaches: hydrogen fuel cells and hydrogen combustion.
In the hydrogen combustion method, gas turbines will be powered by hydrogen, using modified fuel injectors and fuel systems similar to those found in current aircraft engines. Alternatively, hydrogen fuel cells will generate electrical energy to drive electric motors, providing a completely different propulsion mechanism compared to traditional aircraft.
Airbus is currently developing several concepts for hydrogen-powered aircraft, including:
- Turbofan Aircraft: Designed to carry up to 200 passengers over 2,000 nautical miles.
- Turboprop Aircraft: A slightly smaller variant accommodating 100 passengers with a range of 1,000 nautical miles.
- Blended-Wing Body (BWB): An ultra-futuristic design offering similar capacity and range to the turbofan.
- All-Electric Design: Comparable in capacity and range to the turboprop.
These innovative designs underline Airbus’s commitment to exploring various propulsion systems to achieve sustainable air travel.
Toshiba’s Expertise in Superconducting Technology
Toshiba brings a wealth of experience in superconducting technology to this partnership. In June 2022, the company unveiled a prototype of a two-megawatt-class superconducting motor for mobility applications, showcasing its potential in various sectors beyond aviation. Toshiba’s advanced research and development capabilities in high current flow and precise motor drive technology position it as a valuable partner for Airbus in this endeavor.
By collaborating, both companies aim to transform aircraft design and performance through the integration of superconducting systems. This cooperation not only advances their individual goals but also aligns with the global push for decarbonization in the aviation industry.
Challenges and Opportunities Ahead
While the potential for superconducting technology in aviation is immense, several challenges remain. The complexity of developing reliable and efficient superconducting motors, along with the practicalities of integrating them into aircraft designs, requires significant research and investment. The cryogenic cooling systems needed to maintain superconductivity must also be robust and efficient.
However, the rewards of overcoming these challenges are substantial. Achieving high levels of energy efficiency and reducing emissions will play a critical role in addressing the aviation industry’s environmental impact. The partnership between Airbus and Toshiba is a crucial step in this journey, highlighting the importance of collaboration in driving technological advancements.
Conclusion
The collaboration between Airbus and Toshiba marks an exciting development in the field of aviation technology. By focusing on superconducting systems for hydrogen-powered aircraft, both companies are positioning themselves at the forefront of the sustainable aviation revolution. The joint efforts to develop a two-megawatt superconducting motor could unlock new possibilities in aircraft design and performance, ultimately contributing to the global goal of achieving net-zero emissions by 2050.
As the aviation industry faces increasing pressure to adopt more sustainable practices, innovations like these will be vital. The journey toward hydrogen-powered flight is not just about technological advancements; it represents a commitment to reshaping the future of aviation for the better. With partnerships like that of Airbus and Toshiba, the dream of sustainable air travel becomes increasingly tangible, paving the way for a cleaner, greener future in the skies.